Information Technology
Software Consulting
ARCNET, THE FIRST LOCAL AREA NETWORK
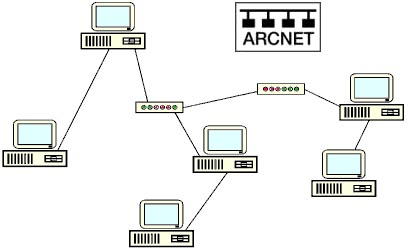
In September 1977, the world's first commercially available local area network
was first put into service at Chase Manhattan Bank, New York, as a beta-site.
Short for Attached Resource Computer network, ARCnet was developed by Datapoint
Corporation in San Antonio, Texas. It was defined as a group of nodes that
communicates to one another over a geographically-limited area usually within
one building or a campus of buildings.
It was the simplest, and least expensive type of local-area network. It used a
token-ring architecture, supported data rates of 2.5 Mbps, and connected up to
255 computers. Node IDs for LAN workstations were typically set by DIP switches
on the network interface card. Larger networks would have to be split into smaller
networks, and bridged. The small number of possible nodes and the need to manually
configure IDs was a disadvantage compared with Ethernet, particularly as large
enterprise networks became common.
A special advantage of ARCnet is that it permitted various types
of transmission media to be mixed on the same network: twisted-pair wire (Max.
extension 150 meters), coaxial cable (650 m.) and fibre optic cable (2.000 m.)